Is a lithium ion
battery still the same as new one after long time storage? With this question, let’s
“reveal the mask” of battery calendar life.
1. What is battery calendar life
Battery’s life usually refers to cycle life and calendar
life (storage life). Among them, the cycle life refers to the time required for
the battery to reach the end of life in working cycles or normal cycles while
the calendar life is defined as: the time required for the battery to reach the
end of life at a certain reference temperature, open state, ie the life of the
battery in standby mode. In summary, calendar life is an assessment of the time
effect on battery’s performance under conditions that minimize battery use.
2. Overview
Studies show that
for a battery calendar life, it’s mainly related to the below factors:
* Battery capacity via storage time
* Battery capacity via storage temperature
* Battery capacity via SOC
* Battery impedance via storage time
2.1 Battery capacity via storage time
It’s
found after testing that the battery capacity is decreasing gradually with the
storage time passing by. The longer the storage time is, the bigger the battery
capacity decays.
This capacity’s degrading can be
attributed to the loss of the inside active lithium.
2.2 Battery
capacity via temperature
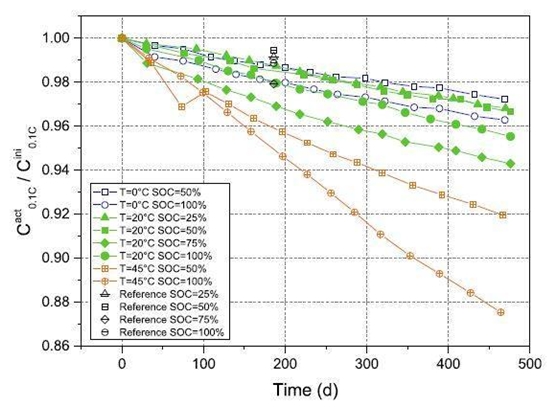
It’s found after testing: a
lithium ion battery with a 50% SOC, the capacity degrading is slightly higher
at 20°C than 0°C. The capacity decay rate at 45°C is twice
that of 20°C. Similar attenuation trends observed at 100% SOC are similar to
trends at 45°C. See below Figure 1:
Figure
1
2.3 Battery capacity via SOC
The 100% SOC cell capacity
decay rate is significantly higher than the 50% SOC cell decay rate, which is
the case at any temperature, as shown in Figure 1. Many studies have found that
high storage SOC accelerates capacity fade. Studies have shown that the low
graphite anode potential at high SOC contributes to electrolyte reduction and
SEI growth, and thus leads to accelerated lithium loss during calendar aging.
At 25% SOC and 75% SOC at 20°C does not obey this trend. The 25% SOC cell has a
faster decline in cell capacity than 50% SOC storage. The cells stored in 75%
SOC are the fastest in capacity degradation in all SOC-level storage cells.
2.4 Battery impedance via storage time
The battery impedance was studied by current pulse measurement and EIS. Current
pulses can determine the overall cell resistance at a certain SOC, temperature,
and current level. The EIS is performed only at open circuit voltage (OCV), but
it describes the change in the electrochemical phenomenon inside the battery in
more detail than the pulse test. See Figure 2.
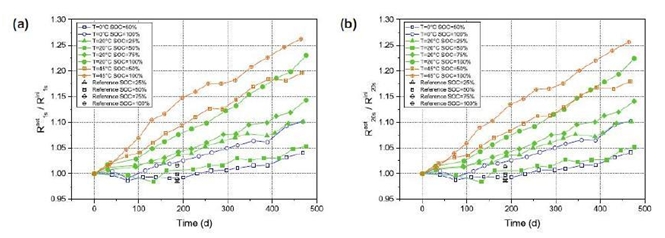
Figure 2
Summery
1. A
newly produced battery after long storage, the performance is degrading. With
the time passing by, its capacity suffers loss, voltage gets down while
impedance gets increased. When the aging reaches a certain degree, the battery is considered to reach its end of life.
2.
If
a battery needs to be stored for a long time without any use, the battery
should be separately stored from the device. And the storage condition: with 50%
SOC at temperature 0~20°C is kindly recommended. Every 3~6 months, it’s
required to cycle (charge & discharge) the battery for 1~3 times to keep
the battery’s inside materials active.
Reference: https://zhuanlan.zhihu.com/p/34218071?utm_medium=social&utm_source=qq

